HTML JavaScript
A Script is a small program which is used with HTML to make web pages more attractive, dynamic and interactive, such as an alert popup window on mouse click. Currently, the most popular scripting language is JavaScript used for websites.
Example:
HTML <script> Tag
The HTML <script> tag is used to specify a client-side script. It may be an internal or external JavaScript which contains scripting statements, hence we can place <script> tag within <body> or <head> section.
It is mainly used to manipulate images, form validation and change content dynamically. JavaScript uses document.getElementById() method to select an HTML element.
Example:
HTML events with JavaScript
An event is something which user does, or browser does such as mouse click or page loading are examples of events, and JavaScript comes in the role if we want something to happen on these events.
HTML provides event handler attributes which work with JavaScript code and can perform some action on an event.
Syntax:
Example:
Output:
Click Event Example
Click on the button and you csn see a pop-up window with a message
HTML can have following events such as:
- Form events: reset, submit, etc.
- Select events: text field, text area, etc.
- Focus event: focus, blur, etc.
- Mouse events: select, mouseup, mousemove, mousedown, click, dblclick, etc.
Following are the list for Window event attributes:
| Event Event Name | Handler Name | Occurs when |
|---|---|---|
| onBlur | blur | When form input loses focus |
| onClick | click | When the user clicks on a form element or a link |
| onSubmit | submit | When user submits a form to the server. |
| onLoad | load | When page loads in a browser. |
| onFocus | focus | When user focuses on an input field. |
| onSelect | select | When user selects the form input filed. |
Note: You will learn more about JavaScript Events in our JavaScript tutorial.
Let's see what JavaScript can do:
1) JavaScript can change HTML content.
Example:
2) JavaScript can change HTML style
Example:
3) JavaScript can change HTML attributes.
Example:
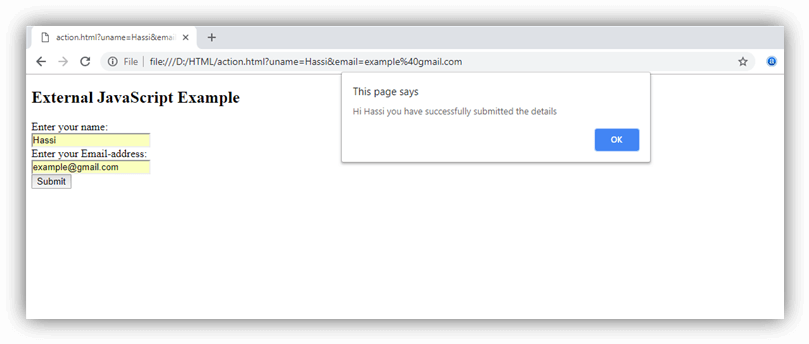
Use External Script
Suppose, you have various HTML files which should have same script, then we can put our JavaScript code in separate file and can call in HTML file. Save JavaScript external files using .js extension.
Note: Do not add <script> tag in the external file, and provide the complete path where you have put the JS file.
Syntax:
Example:
JavaScript code:
Output:
HTML <noscript> Tag
HTML <noscript> tag is used to write disabled script in the browser. The text written within <noscript></noscript> tag is not displayed on the browser.



 Aondover Pascal. O
Aondover Pascal. O
0 Comments