HTML URL Encode
What is URL?
URL stands for Uniform Resource Locator. It is actually a web address. A URL can contain words i.e. (javatpoint.com) or an Internet Protocol (IP) address i.e.195.201.68.81. But most of the user use URL in the form of words because it is easy to remember than numbers.
Syntax of a URL:
Here,
- scheme is used to define the type of Internet service (most common is http or https).
- prefix is used to define a domain prefix (default for http is www).
- domain is used to define the Internet domain name (like javaTpoint.com).
- port is used to define the port number at the host (default for http is 80).
- path is used to define a path at the server (If omitted: the root directory of the site).
- filename is used to define the name of a document or resource.
Following is a list of some common types of schemes used in URL:
http(HyperText Transfer Protocol):Common web pages. Not encrypted.
- https (Secure HyperText Transfer Protocol):Secure web pages. Encrypted.
- ftp(File Transfer Protocol): Downloading or uploading files.
- file: A file on your computer.
URL Encoding
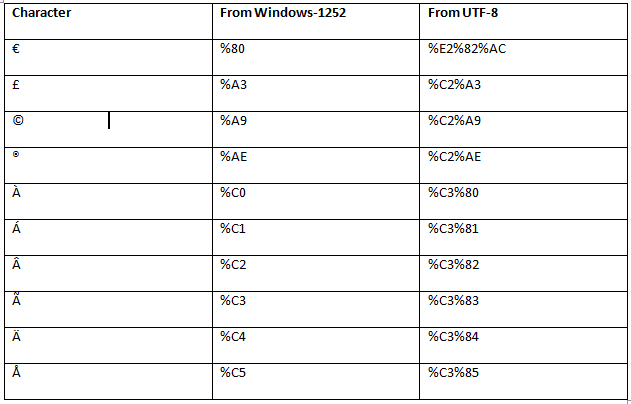
URL encoding is used to convert non-ASCII characters into a format that can be used over the Internet because a URL is sent over the Internet by using the ASCII character-set only. If a URL contains characters outside the ASCII set, the URL has to be converted.
In URL encoding, the non-ASCII characters are replaced with a "%" followed by hexadecimal digits.
URLs cannot contain spaces. URL encoding normally replaces a space with a plus (+) sign, or %20.
Following is a list of some character sets which are encoded by browser after submitting the text.



 Aondover Pascal. O
Aondover Pascal. O
0 Comments